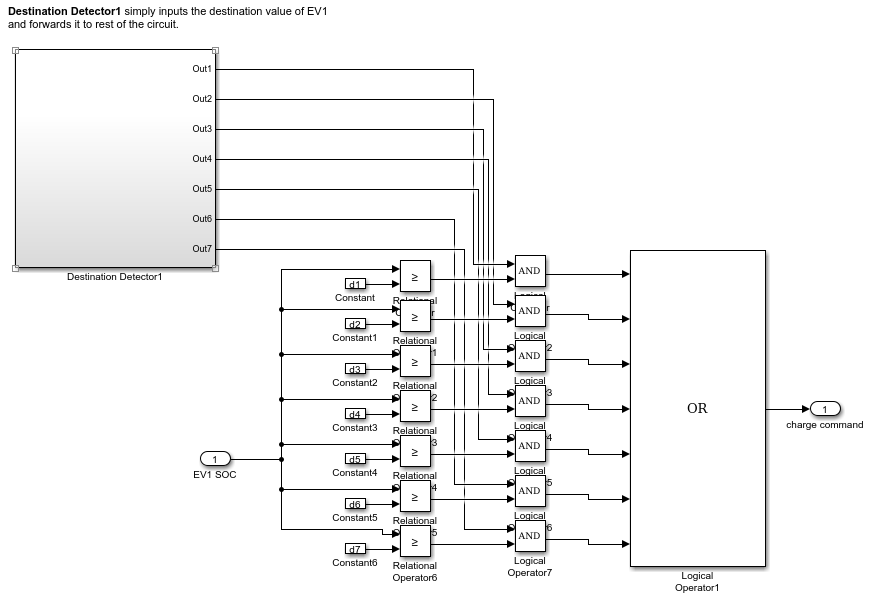
WWe knew mobiles can charge each other and which led me to think, EV are going to be as ubiquitous as mobiles in the future. What if EVs can charge each other? My university has less parking space, what if I develop a scheme for sharing the cars? We did simulations for the implementation of the same in the academic setting of the Birla Institute of Technology and Science, using seven distinct destination points and fast charging posts based on a battery to battery charging system (B to B) where series charging is used. The system uses real world data collected from the college campus and a model was developed for the same to demonstrate the experiment that we conducted.
A 3 level charging system is used for the same with ac, dc and fast charging method mode. Enabling charging in less than an hour and prediction logic circuits are developed for helping remove psychological ‘anxiety; issues of the drivers for the required distance to be covered
The data set points required for the experiment was derived after analysing car parking status in the lot for a week and using relevant records mentained by praking guard
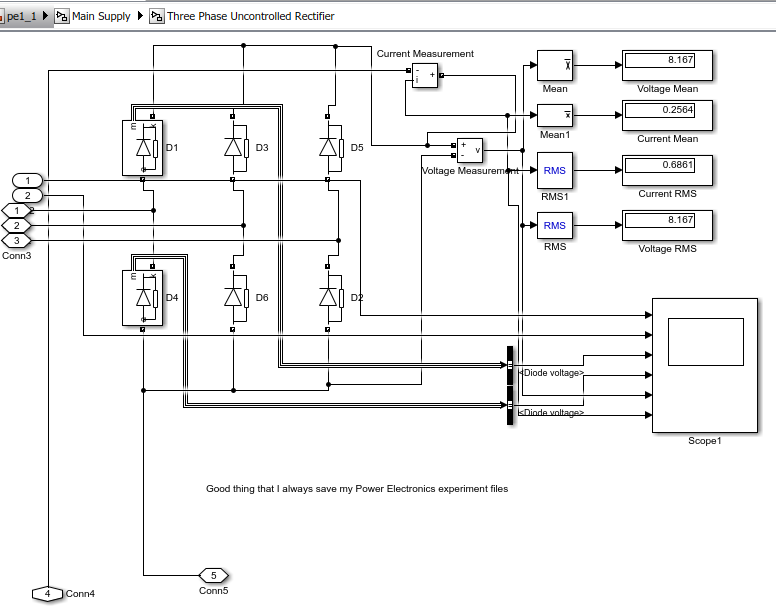
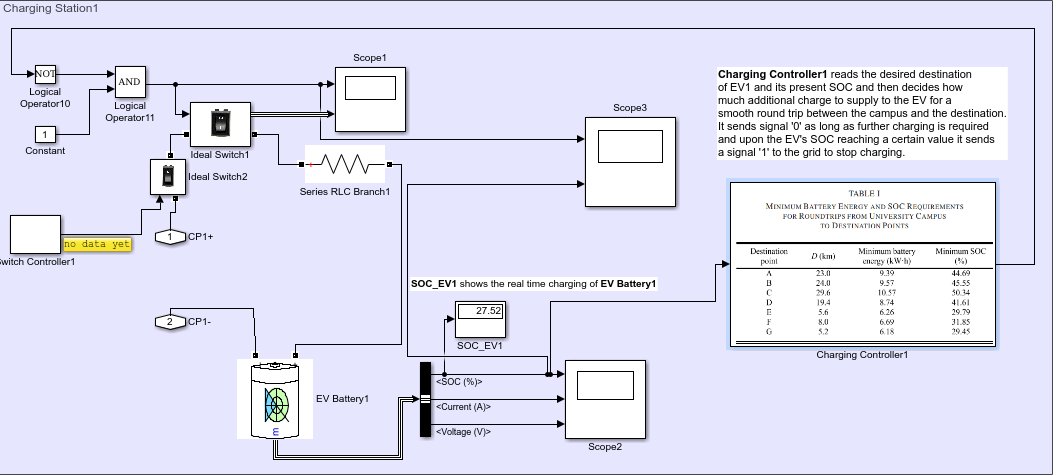
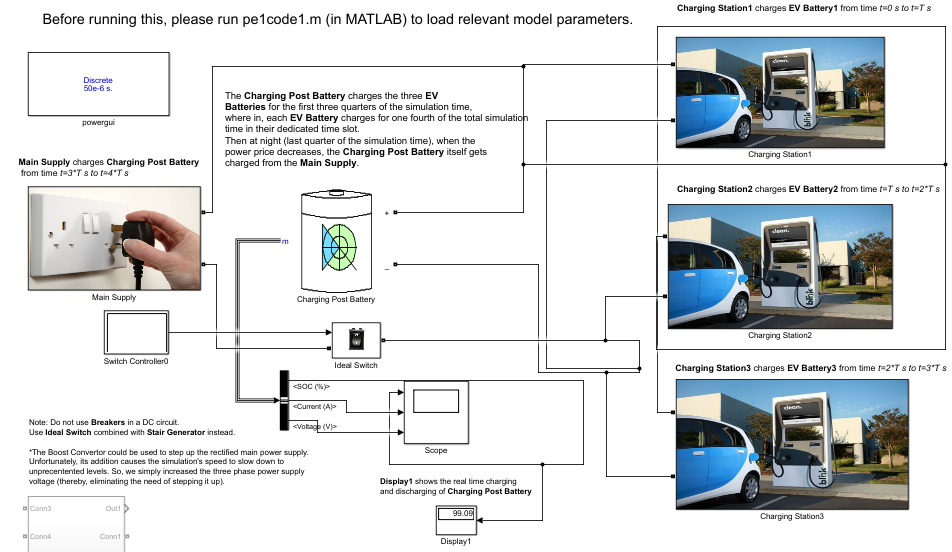
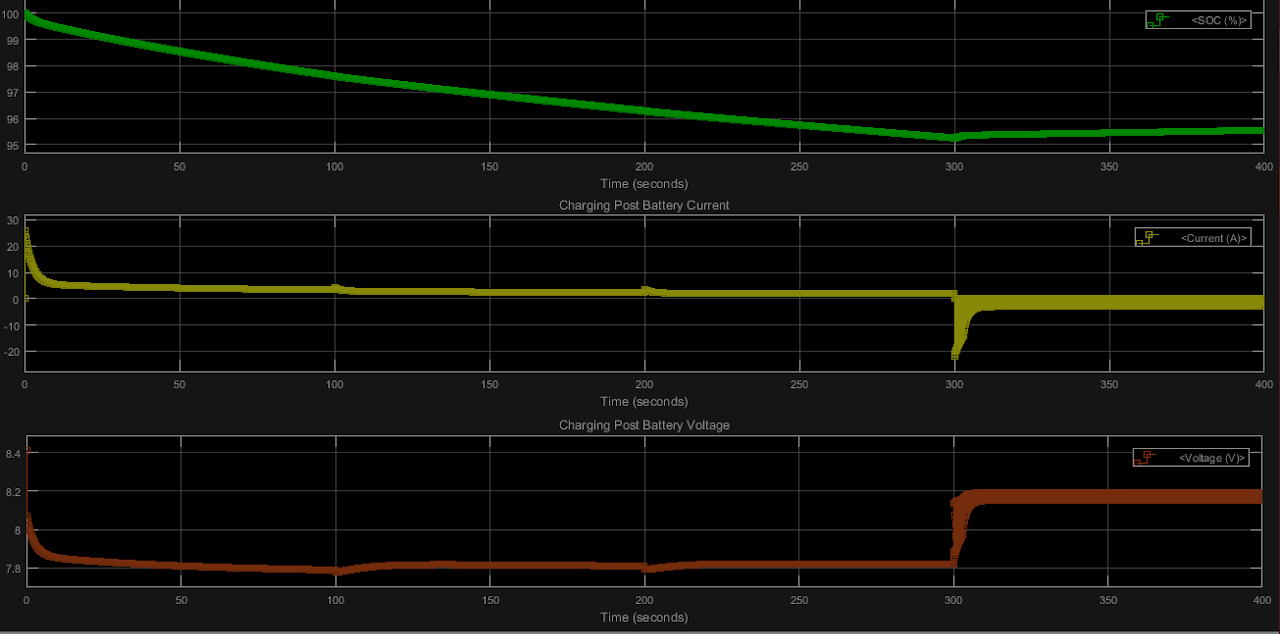
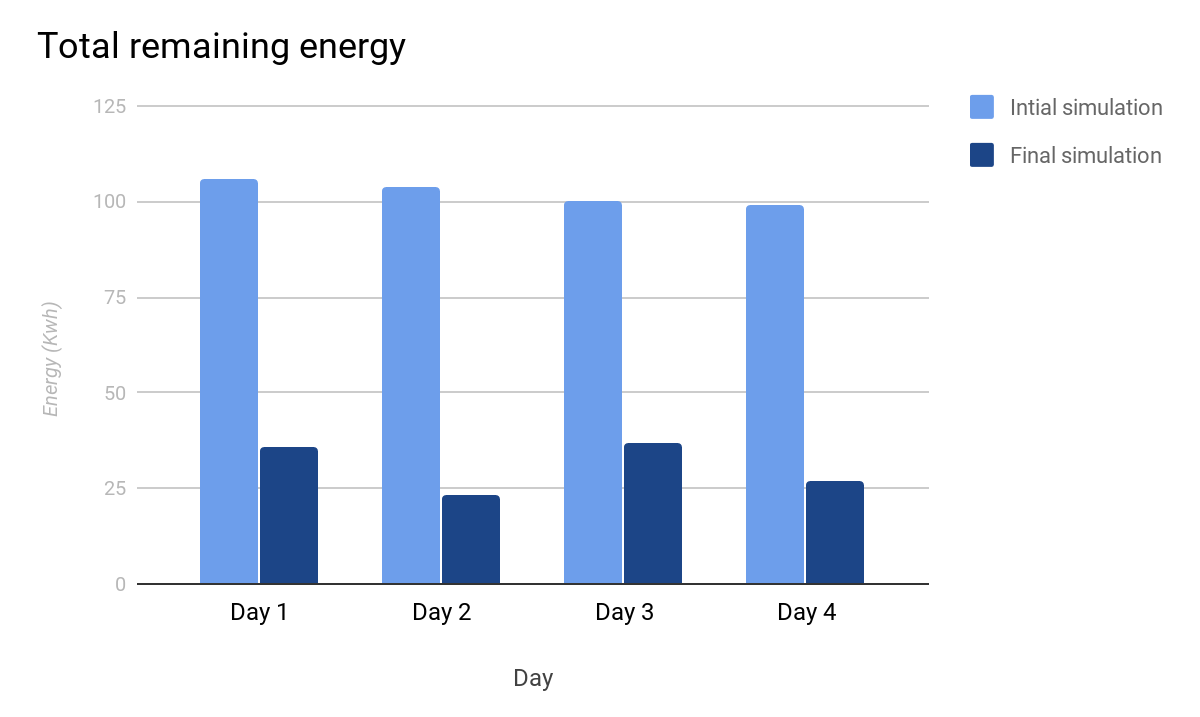
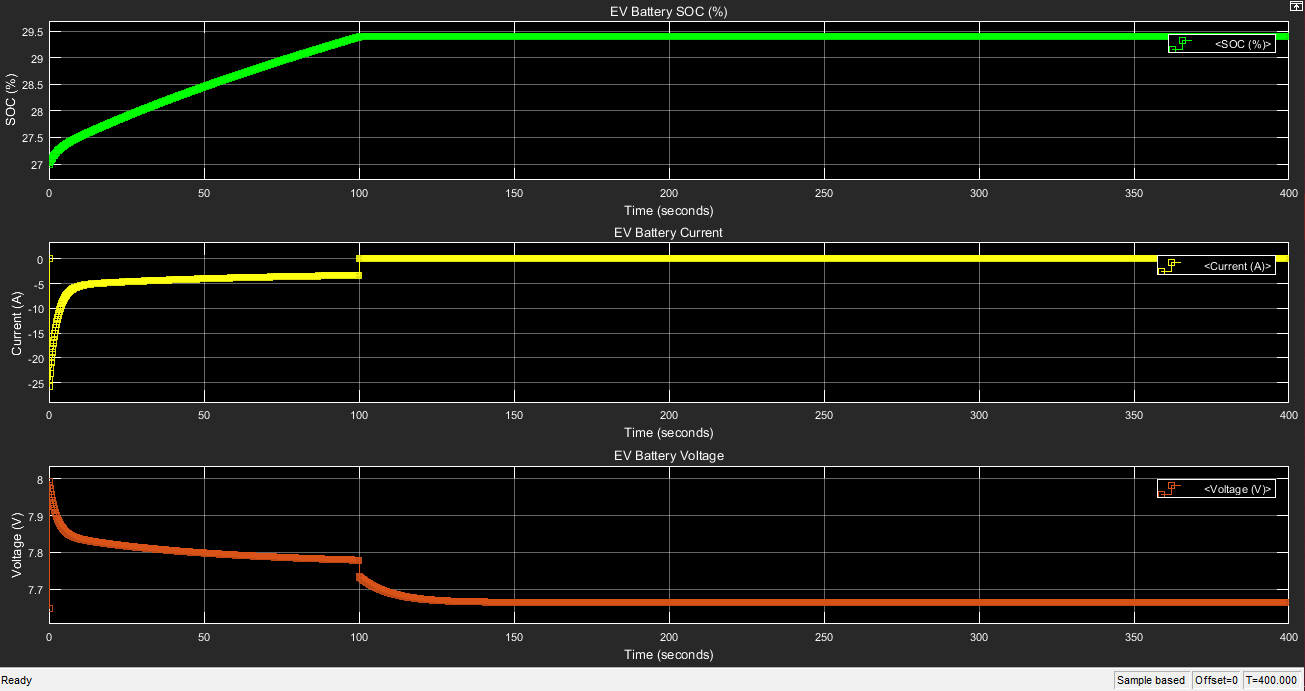
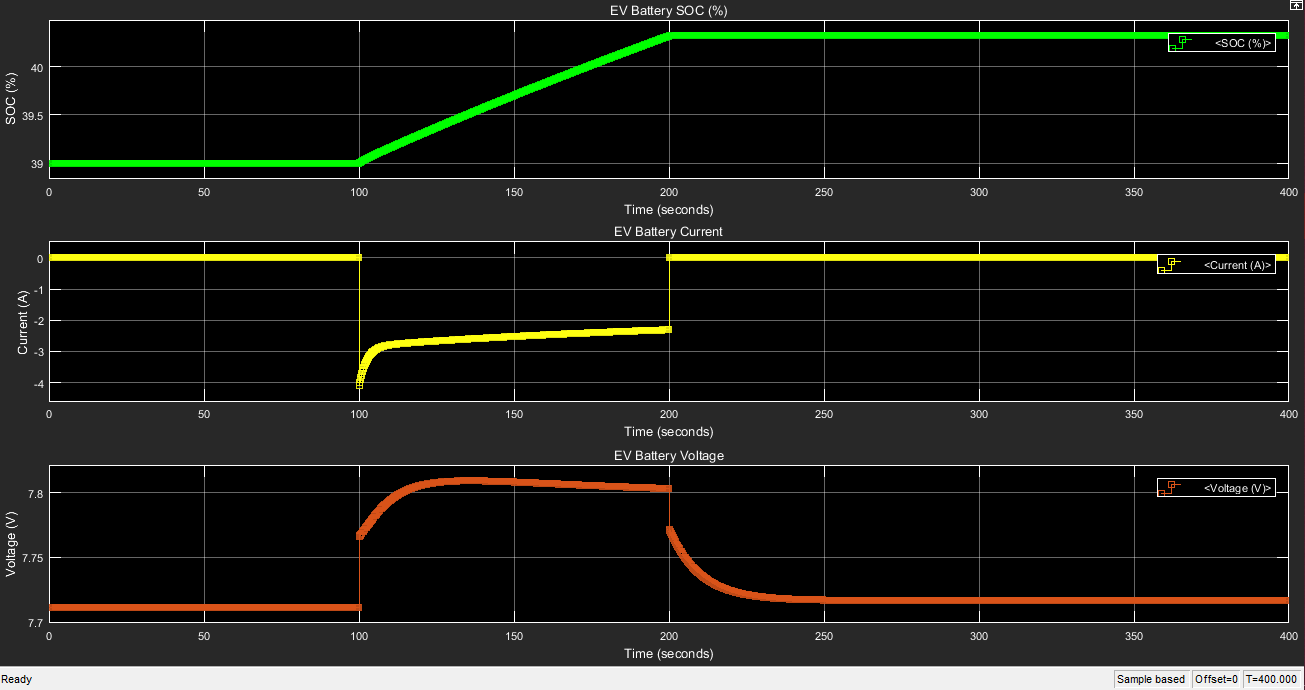
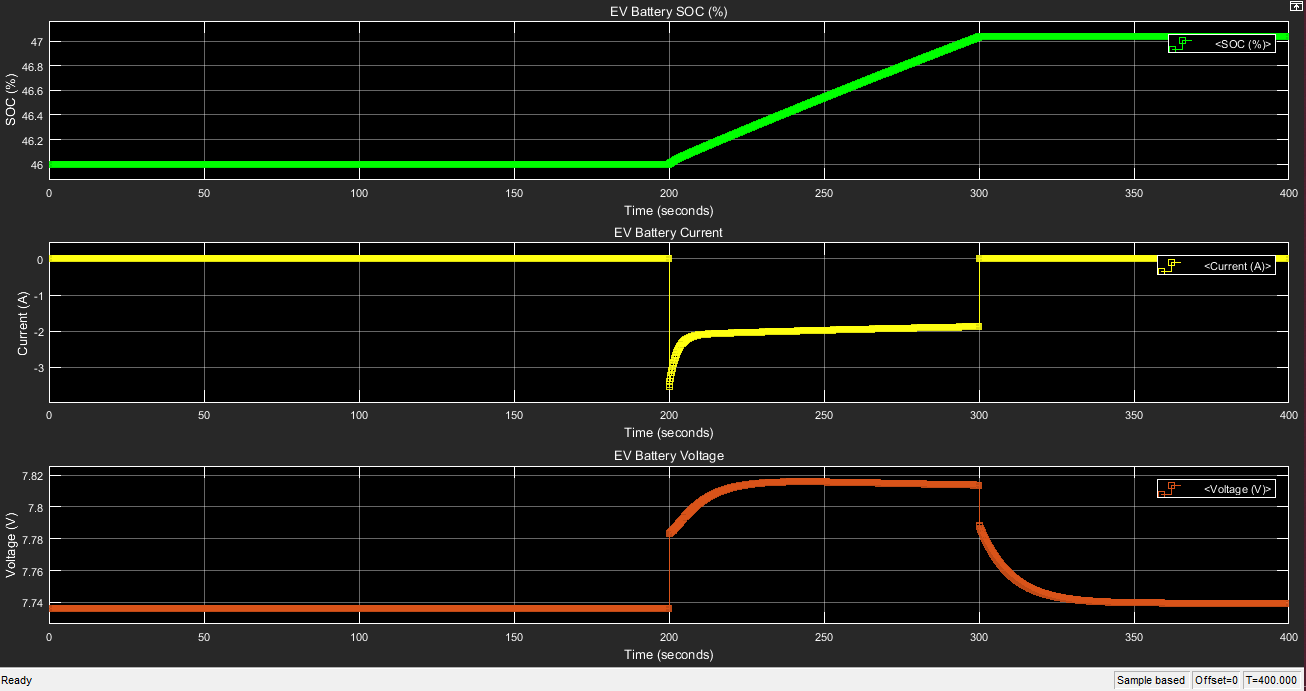
TThe aim is to have longer run time of the EV battery to keep it on the roas for as long as possible. The time for charging is to be reduced along with maximising availability of the vehicles for the maximum time.
the design aspects of a fast charging statoion for the carsharing system with three EVs to help with the commutation inside the academic setting of BITS-Pilani hyderabad campus. The data from the parking lot served as the data extraction set point such as the destination for the vehicles and average parking time used by the EV.
Ev to ev charging requires appropriate converters for changing from dc to dc (buck boost), we want the batteries to charge as soon as possible and again be able to charge themselves at the the stations based on state of charge to mentain net positive supply! The questions that this enables is can we now charge beyond just brakes? Can recharging be done in other idle staates of charges? If EVs can be charged this way a network of services can started with commutation basically automated and on demand, with fleets of autonomous cars. Can we make such a fleet work also in case of UAVs to enable docking and charging. This can in future allow for long range UAV transports, mid air dock and charge and enable wider range of possibilities with regards to supply chain (delivery systems automated with fleet of drones), surveillance, swarm based opoerations,etc. What this also opens up is a possibility of vehicles just differentiated based on their type of motors since the battery storage technology remains exactly yhe same and converters can jack up or lower voltage for transformation on will!